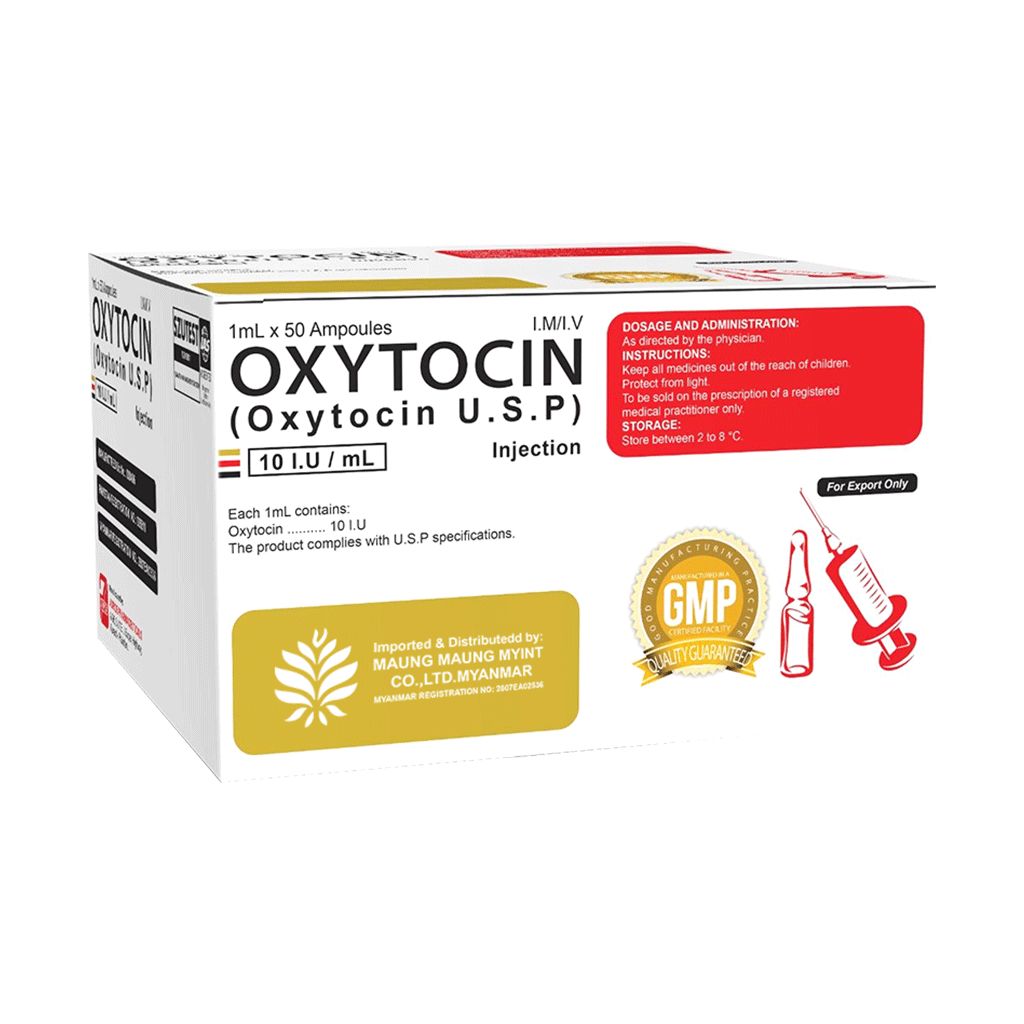
Oxytocin Injection (U.S.P)
10 IU/mL
Certified and trusted by healthcare professionals across Myanmar
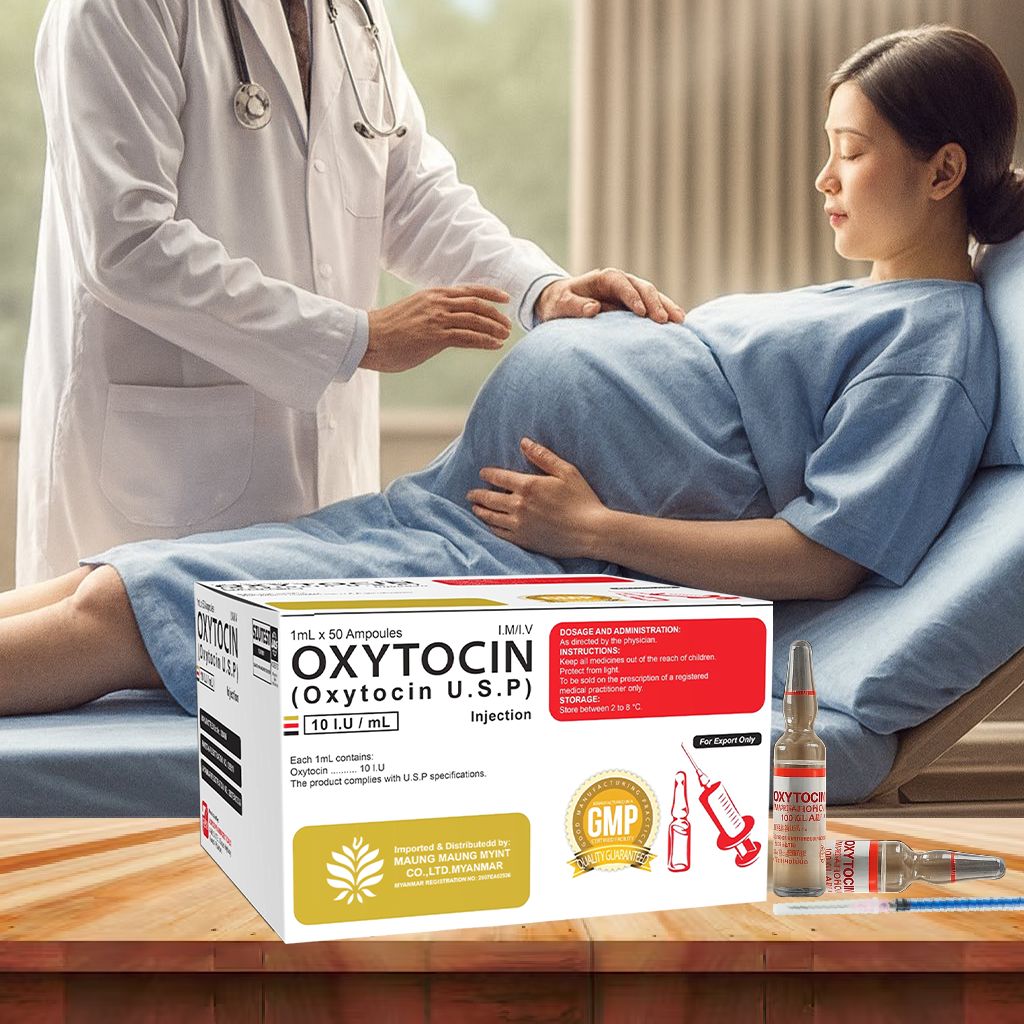
Product Overview
Type
Injectable Solution
Packaging
1 ml <= 50 Ampoules / Box
Strength
10 I.U. / mL
Administration Route
I.M, / I.V
Storage Conditions
Store at 2*C to 8*C
Regulatory Approvals
FDA Myanmar, WHO-GMP
Benefits
- Facilitates labor induction
- Enhances labor progress
- Controls postpartum bleeding
- Quick onset & reliable action
- Backed by medical professionals
Maung Maung Myint Co., Ltd is committed to delivering high-quality Oxytocin, approved for hospital and medical use across Myanmar